OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Zaktualizowano Autocorrelation Oscillator
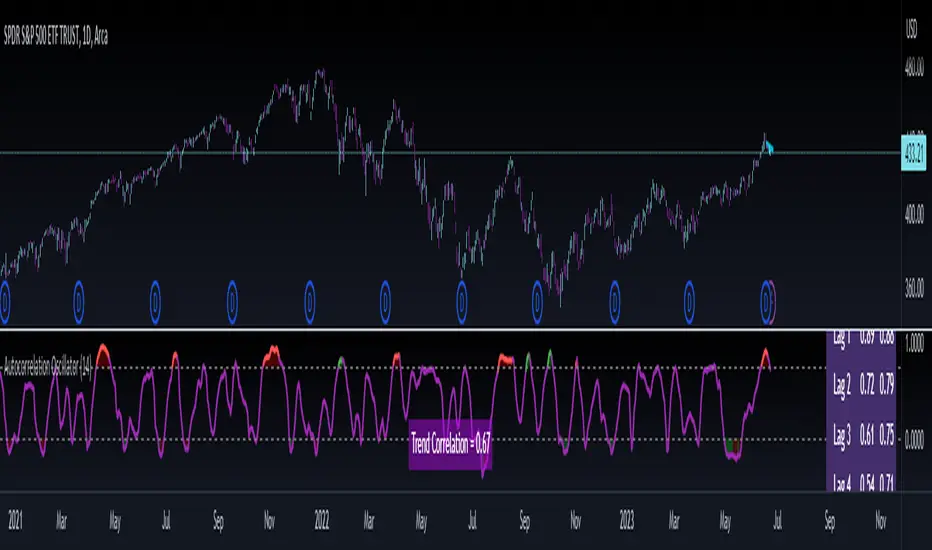
Releasing the autocorrelation oscillator.
NOTE! Please be sure to read the description. This is a theoretical indicator and its important to understand the theory behind its use.
About the indicator:
Before getting into the indicator and its functionality, its important to discuss the theoretical underpinnings of the indicator.
The autocorrelation oscillator operates on two theories of market behaviour that go hand in hand. Those theories are the market efficiency theory and the random walk theory (or hypothesis ).
Market efficiency theory: The market efficiency theory or "Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)" postulates that all available information is reflected in a ticker's price almost instantaneously and thus it is impossible for an investor or trader to get ahead of the market because we cannot respond to the speed that the market responds. Of course, there are many holes in this theory, the most notable being that the market is a function of humans. Absent humans and their technological integrations into the market, the market would cease to react at all. But that's besides the point. This is a widely accepted theory and one in which I can mathematically observe through statistical tests. The truth behind this theory is the market is efficient for responding to evolving economic and financial information, likely owning to huge amounts of computer and algorithmic integration into trading, and thus the market is more efficient than the average person is capable (absent computerized algorithms and integration) of ascertaining nuanced financial and economic circumstances. By the time we the people can appraise information, the market has already acted on it. And that is the main premise of the EMH.
The next theory is the Random Walk Theory or Hypothesis (RWH). This builds on the EMH and essentially postulates that the market reacts so quickly to price in current circumstances that it is too random for people to truly exploit and benefit from.
The result of these two theories is two-fold and can be summarized as such:
a) The market behaves in a chaotic fashion that is seemingly random and is incapable of being predicted effectively; and
b) The market is more efficient than a person in incorporating key fundamental information, contributing to the high degree of seemingly random behaviour.
So, how does this help us?
It is said, because of the EMH and the RWH, the only way to truly exploit the market for profit is by:
a) Buying and holding and investing under the bias that stocks will eventually rise in value; or
b) For short term trading, exploiting the pricing anomalies within the data.
So how do we exploit pricing anomalies within the data?
Well, in my own research on market efficiency and behaviour, I have identified many ways of figuring out some anomalies. One of the most effective ways is by looking at simple correlation of lagged values, or autocorrelation for short.
What is autocorrelation and how to use it in relation to EMH and RWH?
Autocorrelation refers to the correlative relationship among the values in a series. Put simply, its the relationship of the same variable over time. For example, if we wanted to look at the auto-correlation of a ticker's high price, we would take, say, 5 to 7 previous high prices and correlate them with the current high price in a series dataset. If the EMH and RWH are true, the correlation among all the variables should have an average less than 0.5 or greater than -0.5. This would indicate true randomness in the dataset and thus an efficient market.
However, if the average of all of the sum's of these correlations are greater than or equal to 0.5 or less than or equal to -0.5, that indicates there is a high degree of autocorrelation and thus the EMH ad RWH is being invalidated as the market is not operating efficiently. This is an anomaly and this anomaly can be exploited.
So how do we exploit it?
Well, when the EMH and RWH hypothesis is being invalidated, we can expect what I coin as a "Regression to Chaos" i.e. the market will revert back to an efficient equilibrium state. So if we have a high correlation of the lagged variables and a strong uptrend or downtrend correlation, we can expect an inefficient market to correct back to an efficient market (i.e. have a reversal from the current trend).
So how does the indicator work?
The indicator measures the lagged correlation of the previous 5 highs and lows of a ticker. A high correlation among all of the highs and lows that exceeds 0.8 would be an invalidation of the EMH and RWH and thus signal a correction to come (i.e. a Regression to Chaos).
The indicator will display this by changing colour. Red for a bearish reversal and green for a bullish. Let's take a look below using the ticker MSFT:

Above we can see the indicator identifying observed inefficiencies within the MSFT ticker on the 1 minute timeframe. The green vertical lines correspond to potential bullish reversals as a result of bearish inefficiencies, the red correspond to bearish reversals as a result of bullish inefficiencies.
You can see these lead to reversals within the ticker.
Components of the indicator:

In the chart above we see the following that are being indicated by arrows:
Red Arrows: Show the identified inefficiencies. Red for bullish inefficiencies (i.e. bearish reversal), green for bearish inefficiencies (i.e. bullish reversal)
Yellow Arrow: The lagged variable chart. This will display the current correlation among all the lagged variables the indicator is assessing.
Teal arrow: Displays the current strength of the trend by correlating the trend to time. A strong negative value (i.e. a value less than or equal to -0.5) indicates a strong downtrend, a strong positive value indicates the inverse.
You can unselect the data-tables in the settings menu if you just want to view the correlation line itself. This part of the indicator is customizable. You can also define the lookback period; however, it is strongly recommended to leave it at 14 as this maintains the use of this indicator as an oscillator.
And that is the indicator! Let me know your comments, questions and feedback below.
Safe trades everyone!
NOTE! Please be sure to read the description. This is a theoretical indicator and its important to understand the theory behind its use.
About the indicator:
Before getting into the indicator and its functionality, its important to discuss the theoretical underpinnings of the indicator.
The autocorrelation oscillator operates on two theories of market behaviour that go hand in hand. Those theories are the market efficiency theory and the random walk theory (or hypothesis ).
Market efficiency theory: The market efficiency theory or "Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)" postulates that all available information is reflected in a ticker's price almost instantaneously and thus it is impossible for an investor or trader to get ahead of the market because we cannot respond to the speed that the market responds. Of course, there are many holes in this theory, the most notable being that the market is a function of humans. Absent humans and their technological integrations into the market, the market would cease to react at all. But that's besides the point. This is a widely accepted theory and one in which I can mathematically observe through statistical tests. The truth behind this theory is the market is efficient for responding to evolving economic and financial information, likely owning to huge amounts of computer and algorithmic integration into trading, and thus the market is more efficient than the average person is capable (absent computerized algorithms and integration) of ascertaining nuanced financial and economic circumstances. By the time we the people can appraise information, the market has already acted on it. And that is the main premise of the EMH.
The next theory is the Random Walk Theory or Hypothesis (RWH). This builds on the EMH and essentially postulates that the market reacts so quickly to price in current circumstances that it is too random for people to truly exploit and benefit from.
The result of these two theories is two-fold and can be summarized as such:
a) The market behaves in a chaotic fashion that is seemingly random and is incapable of being predicted effectively; and
b) The market is more efficient than a person in incorporating key fundamental information, contributing to the high degree of seemingly random behaviour.
So, how does this help us?
It is said, because of the EMH and the RWH, the only way to truly exploit the market for profit is by:
a) Buying and holding and investing under the bias that stocks will eventually rise in value; or
b) For short term trading, exploiting the pricing anomalies within the data.
So how do we exploit pricing anomalies within the data?
Well, in my own research on market efficiency and behaviour, I have identified many ways of figuring out some anomalies. One of the most effective ways is by looking at simple correlation of lagged values, or autocorrelation for short.
What is autocorrelation and how to use it in relation to EMH and RWH?
Autocorrelation refers to the correlative relationship among the values in a series. Put simply, its the relationship of the same variable over time. For example, if we wanted to look at the auto-correlation of a ticker's high price, we would take, say, 5 to 7 previous high prices and correlate them with the current high price in a series dataset. If the EMH and RWH are true, the correlation among all the variables should have an average less than 0.5 or greater than -0.5. This would indicate true randomness in the dataset and thus an efficient market.
However, if the average of all of the sum's of these correlations are greater than or equal to 0.5 or less than or equal to -0.5, that indicates there is a high degree of autocorrelation and thus the EMH ad RWH is being invalidated as the market is not operating efficiently. This is an anomaly and this anomaly can be exploited.
So how do we exploit it?
Well, when the EMH and RWH hypothesis is being invalidated, we can expect what I coin as a "Regression to Chaos" i.e. the market will revert back to an efficient equilibrium state. So if we have a high correlation of the lagged variables and a strong uptrend or downtrend correlation, we can expect an inefficient market to correct back to an efficient market (i.e. have a reversal from the current trend).
So how does the indicator work?
The indicator measures the lagged correlation of the previous 5 highs and lows of a ticker. A high correlation among all of the highs and lows that exceeds 0.8 would be an invalidation of the EMH and RWH and thus signal a correction to come (i.e. a Regression to Chaos).
The indicator will display this by changing colour. Red for a bearish reversal and green for a bullish. Let's take a look below using the ticker MSFT:
Above we can see the indicator identifying observed inefficiencies within the MSFT ticker on the 1 minute timeframe. The green vertical lines correspond to potential bullish reversals as a result of bearish inefficiencies, the red correspond to bearish reversals as a result of bullish inefficiencies.
You can see these lead to reversals within the ticker.
Components of the indicator:
In the chart above we see the following that are being indicated by arrows:
Red Arrows: Show the identified inefficiencies. Red for bullish inefficiencies (i.e. bearish reversal), green for bearish inefficiencies (i.e. bullish reversal)
Yellow Arrow: The lagged variable chart. This will display the current correlation among all the lagged variables the indicator is assessing.
Teal arrow: Displays the current strength of the trend by correlating the trend to time. A strong negative value (i.e. a value less than or equal to -0.5) indicates a strong downtrend, a strong positive value indicates the inverse.
You can unselect the data-tables in the settings menu if you just want to view the correlation line itself. This part of the indicator is customizable. You can also define the lookback period; however, it is strongly recommended to leave it at 14 as this maintains the use of this indicator as an oscillator.
And that is the indicator! Let me know your comments, questions and feedback below.
Safe trades everyone!
Informacje o Wersji
Quick fix!Skrypt open-source
W zgodzie z duchem TradingView twórca tego skryptu udostępnił go jako open-source, aby użytkownicy mogli przejrzeć i zweryfikować jego działanie. Ukłony dla autora. Korzystanie jest bezpłatne, jednak ponowna publikacja kodu podlega naszym Zasadom serwisu.
Get:
- Live Updates,
- Discord access,
- Access to my Proprietary Merlin Software,
- Access to premium indicators,
patreon.com/steversteves
Now on X!
- Live Updates,
- Discord access,
- Access to my Proprietary Merlin Software,
- Access to premium indicators,
patreon.com/steversteves
Now on X!
Wyłączenie odpowiedzialności
Informacje i publikacje nie stanowią i nie powinny być traktowane jako porady finansowe, inwestycyjne, tradingowe ani jakiekolwiek inne rekomendacje dostarczane lub zatwierdzone przez TradingView. Więcej informacji znajduje się w Warunkach użytkowania.
Skrypt open-source
W zgodzie z duchem TradingView twórca tego skryptu udostępnił go jako open-source, aby użytkownicy mogli przejrzeć i zweryfikować jego działanie. Ukłony dla autora. Korzystanie jest bezpłatne, jednak ponowna publikacja kodu podlega naszym Zasadom serwisu.
Get:
- Live Updates,
- Discord access,
- Access to my Proprietary Merlin Software,
- Access to premium indicators,
patreon.com/steversteves
Now on X!
- Live Updates,
- Discord access,
- Access to my Proprietary Merlin Software,
- Access to premium indicators,
patreon.com/steversteves
Now on X!
Wyłączenie odpowiedzialności
Informacje i publikacje nie stanowią i nie powinny być traktowane jako porady finansowe, inwestycyjne, tradingowe ani jakiekolwiek inne rekomendacje dostarczane lub zatwierdzone przez TradingView. Więcej informacji znajduje się w Warunkach użytkowania.